World Economic Forum (WEF) announced the results of its first global simulation in October, 2019, predicting a catastrophic pandemic. Months later the world was hit with COVID. Their latest sim predicts a worldwide cyber attack targeting financial and health operations, creating an even greater health crisis.
Whether feasible or fable, building operational resiliency and digital security in today’s unstable world remains good risk management.
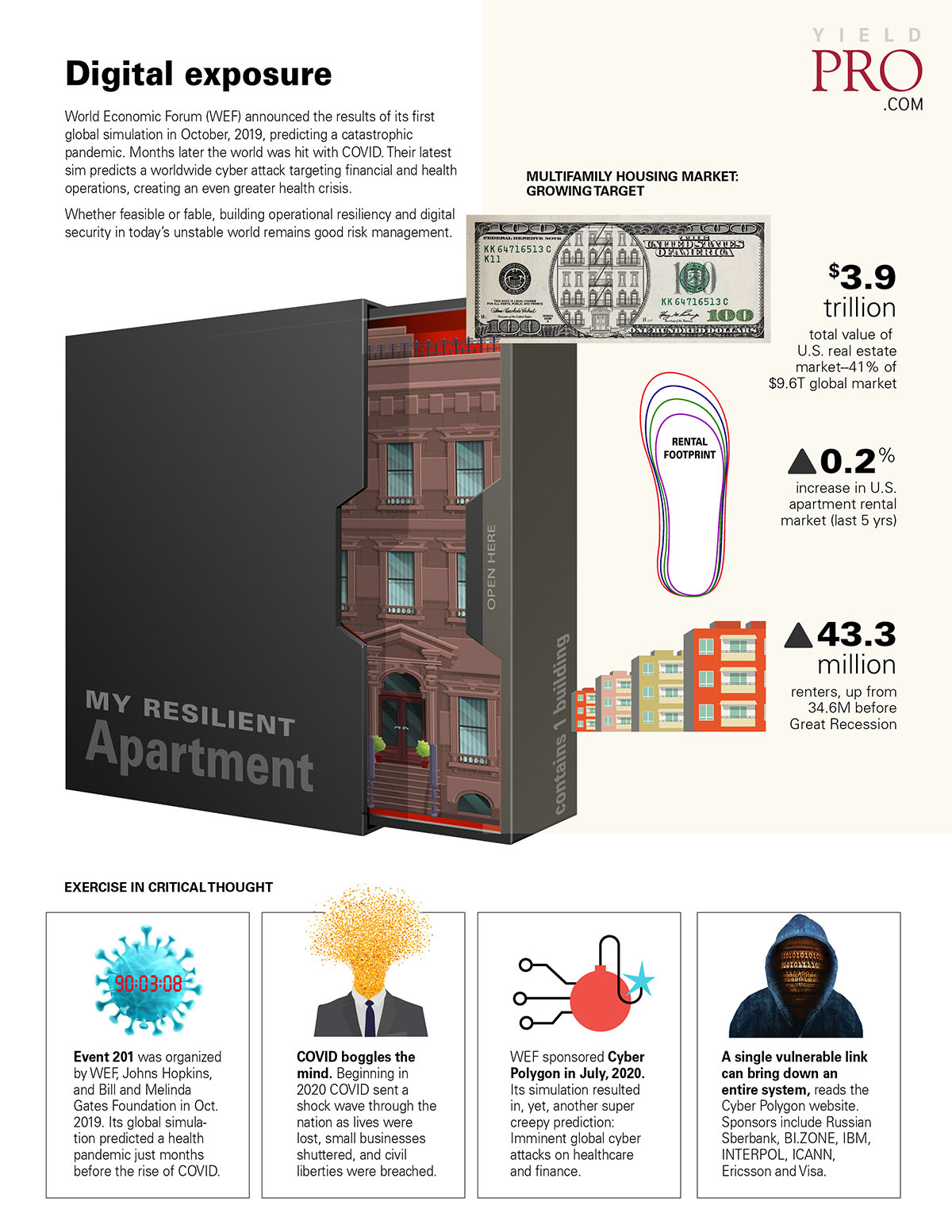
Multifamily housing market: growing target
- $3.9 trillion total value of U.S. real estate market—41% of $9.6T global market
- 2% increase in U.S. apartment rental market (last 5 yrs.)
- 3 million renters, up from 34.6M before Great Recession
- 6% U.S. market are renters (2021) a 50 year high
- $485 billion are paid in U.S. rents each year; 34% of these are paper checks
- 23% growth of card-not-present transactions y/y. Fastest growing category: Account-to-account showed 59% y/y growth
Exercise in critical thought
Event 201 was organized by WEF, Johns Hopkins, and Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation in Oct. 2019. Its global simulation predicted a health pandemic just months before the rise of COVID.
COVID boggles the mind. Beginning in 2020 COVID sent a shock wave through the nation as lives were lost, small businesses shuttered, and civil liberties were breached.
WEF sponsored Cyber Polygon in July, 2020. Its simulation resulted in, yet, another super creepy prediction: Imminent global cyber attacks on healthcare and finance.
A single vulnerable link can bring down an entire system, reads the Cyber Polygon website. Sponsors include Russian Sberbank, BI.ZONE, IBM, INTERPOL, ICANN, Ericsson and Visa.
U.S.: zero trust architecture
In May, Pres. Biden issued an Executive Order partnering Feds with Big Tech to find and address cyber threats. In August, the president met with IBM, Microsoft, Amazon, Google and others to help reset security protocols, especially for infrastructure and supply chains.
In August, the FBI and the Cyber- security Infrastructure Security Agency issued a warning on rising ransomware attacks, especially through email. Hive thieves are one example. They invade, issue a ransom demand, and threaten to publish data on the Tor site, HiveLeaks.
$13.7 billion. The cost of cyberattacks to the U.S. government. The U.S. suffered the most financial damage of any country (2018). Proposed U.S. budget for cyber security (2021) is $18.78 billion, and $88.78 billion for IT.
Many private sector companies have yet to sufficiently harden their defenses. Russian-based Darkside got into Colonial Pipeline networks using an inactive Virtual Private Network log-in found among stolen passwords on the dark web.
By the numbers
95% of cyber security breaches are caused by human error. The average cost of a data breach is $3.86 million. The average time to identify a breach is 280 days from identification to containment. (2020)
36 billion records. Number of records exposed through data breaches in the first half of 2020. An estimate 300 billion passwords are used by humans and machines globally
Basic internet hygiene: deactivating old accounts, mandating frequent password updates and two-factor user authentication, and running company operations from backup data would protect against most hacks.
Some argue that private companies should be able to retaliate.
Congressionally issued letters of marque were granted to merchant ships to recover stolen assets from pirates in the 18th century. A modern version would allow corporations to scout and share data with U.S. agencies in return for immunity.